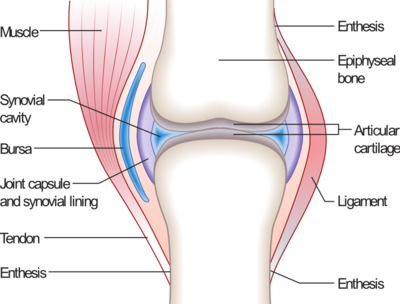
Synovial joints
* Structure :
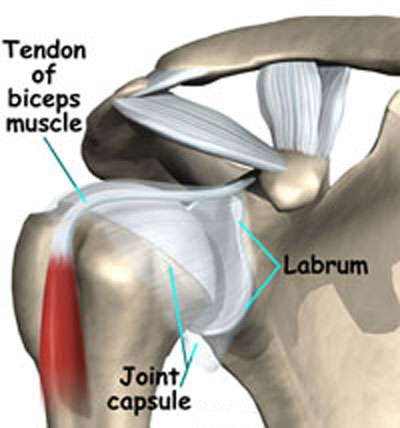
- The joint is enveloped by fibrous capsule.
- The capsule is thickened in some places forming ligaments.
- The capsule is lined with synovial membrane.
- The articular surface of the bone is covered by articular cartilage.
- The joint cavity contains synovial fluid.
- The joint cavity may contain other additional intracapsular structures like
inter-articular disc, labrum, meniscus or tendons of muscles.
* Classification :
( According to the number of axes around which movements occur )
- Uni-axial joints ( one axis ) :
- Hinge joints : transverse axis > flexion and extension > elbow joint
- Pivot joints : vertical axis > rotation > radio-ulnar joint
- Bi-axial joints ( two axes ) :
- Ellipsoid joints : flexion, extension, adduction and abduction > wrist joint
- Saddle joints : flexion, extension, adduction, abduction and slight rotation > carpo-metacarpal joint of the thumb.
- Multi-axial joints ( more than two axes ) :All types of movement are allowed > shoulder and hip joints.
- Other types :
- Plane joints : the articular surface are flat > just gliding > intercarpal joints.
- Compound joints : more than one type in the same joint > tempro-mandibular joint.










0 comments:
Post a Comment